
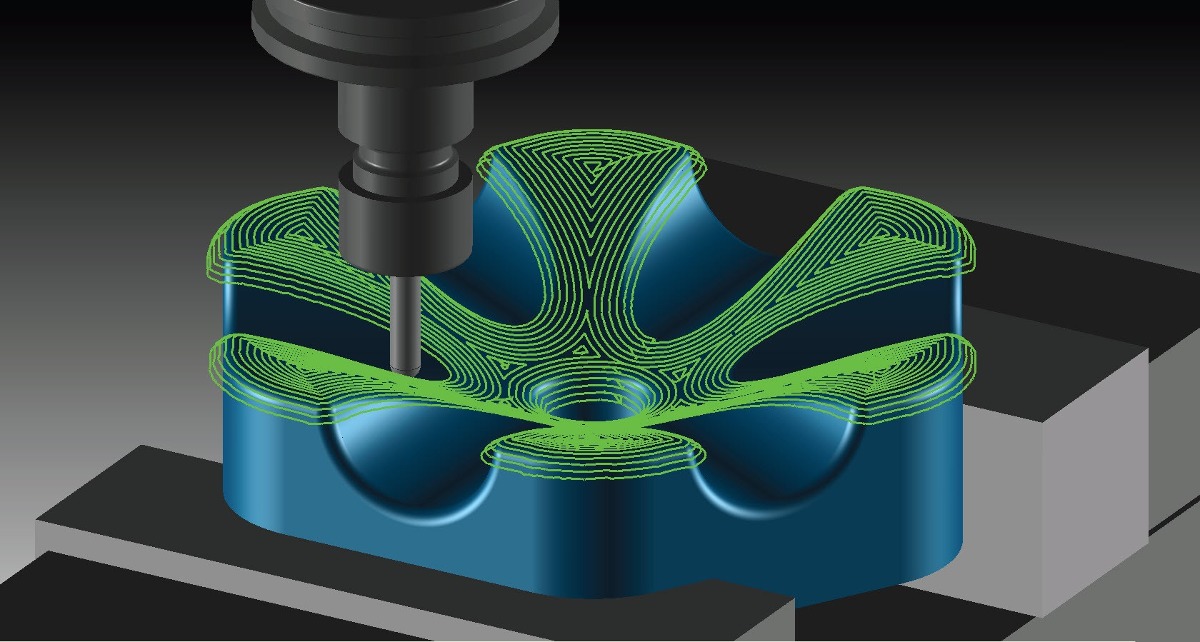
In a Universal Joint mate, the rotation of one component (the output shaft) about its axis is driven by the rotation of another component (the input shaft) about its axis. You can select an axis, cylindrical face, or a slot to create slot mates. You can mate bolts to straight or arced slots and you can mate slots to slots. The components do not need to have gear teeth.Ī Screw mate constrains two components to be concentric, and also adds a pitch relationship between the rotation of one component and the translation of the other component.

You can mate any two components to have this type of movement relative to each other. With rack and pinion mates, linear translation of one component (the rack) causes circular rotation in another component (the pinion), and vice versa. You can limit the angular movement between the two components. It has the same effect as adding a concentric mate plus a coincident mate. Valid selections for the axis of rotation for gear mates include cylindrical and conical faces, axes, and linear edges.Ī hinge mate limits the movement between two components to one rotational degree of freedom. Gear mates force two components to rotate relative to one another about selected axes. It allows you to mate a cylinder, plane, or point to a series of tangent extruded faces, such as you would find on a cam. The NC tab in the Operation Parameters dialog box and the interface of the Technology Database have updated and rearranged labels to improve the readability of CNC finish parameters.A cam-follower mate is a type of tangent or coincident mate.

The Tool Select Filter dialog box lets you enter text to filter for mill and turn tools and assemblies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
